Types of IPv6 Addresses and Their First Hex Digit(s)
IPv6 defines three address types
- unicast
- multicast
- anycast
1- Unicast Addresses
IPv6 includes two different unicast address assignments:
- Global unicast address
- Link-local address
Global Unicast address (Begin with 2)
The global unicast address is globally unique in the Internet, begin with 2 or 3.

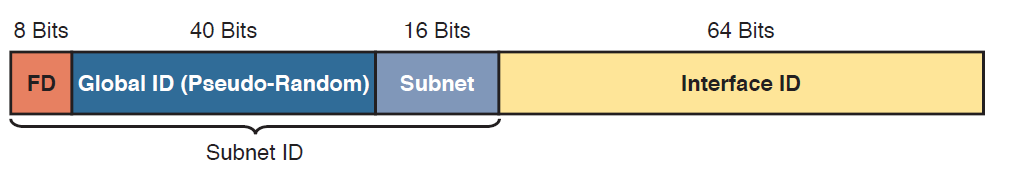
Unique Local Unicast Addresses (Begin with FD)
Unique local addresses begin with hex FD
Link-Local Addresses (Begin with FE80)
- Unicast (not multicast): Link-local addresses represent a single host, and packets sent to a link-local address should be processed by only that one IPv6 host.
- Forwarding scope is the local link only: Packets sent to a link-local address do not leave the local data link because routers do not forward packets with link-local destination addresses.
- Automatically generated: Every IPv6 host interface (and router interface) can create its own link-local address automatically, solving some initialization problems for hosts before they learn a dynamically learned global unicast address.
- Common uses: Link-local addresses are used for some overhead protocols that stay local to one subnet and as the next-hop address for IPv6 routes. Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP), which replaces the functions of IPv4’s ARP, uses link-local addresses.
- Creating Link-Local Addresses on Routers
- First 10 bits must match prefix FE80::/10
- Next 54 bits should be binary 0 – FE80:0000:0000:0000
- The second half of the link-local address; Cisco routers use the EUI-64 format

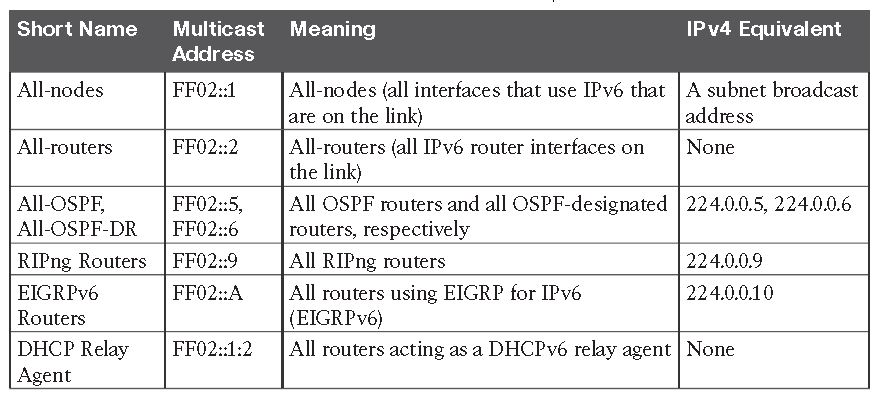
IPv6 Multicast Addresses (Begin with FF)
1- Local Scope Multicast Addresses
Multicast addresses that begin FF08 (FF08::/16) have a link-local scope, meaning that routers will not forward these packets outside the local subnet—which is good.
Key IPv6 Local-Scope Multicast Addresses
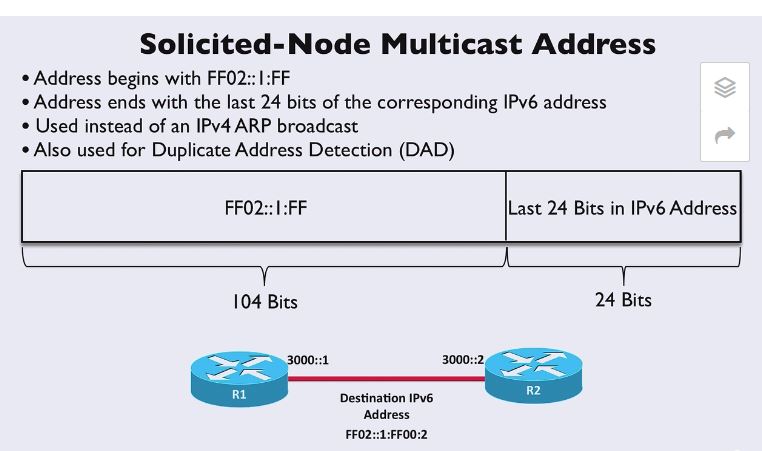
2- Solicited Multicast address
has same first 104 bit address FF02::1:FF
Unspecified IPv6 address (::/128)
A host can use the unknown address (::) when its own IPv6 address is not yet known, or when the host wonders if its own IPv6 address might have problems.
loopback IPv6 address (::1/128)
The IPv6 loopback address gives each IPv6 host a way to test its own protocol stack. Just like the IPv4 127.0.0.1 loopback address,
